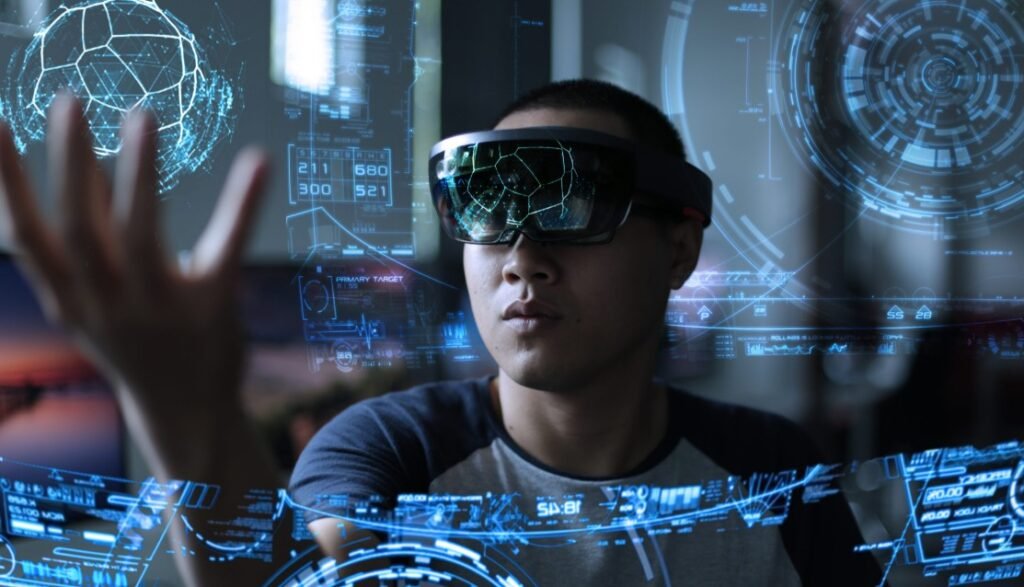
Virtual Reality (VR) has long been associated with gaming and entertainment, but its potential stretches far beyond immersive digital worlds. Today, VR is poised to transform how we work, learn, shop, and even socialize. From education to healthcare, the integration of VR into daily routines is not just a futuristic concept; it’s an evolving reality that promises to reshape everyday life in ways we are only beginning to understand.
One of the most transformative applications of VR is in education. Traditional learning environments often rely on textbooks and lectures, which can leave abstract concepts difficult to grasp. VR offers immersive experiences where students can explore the human body, travel through historical events, or experiment with physics in a fully interactive environment. For instance, medical students can practice surgeries in VR without risking real-life consequences, enhancing their skills and confidence. Similarly, VR-enabled classrooms allow learners from different parts of the world to collaborate in shared virtual spaces, making global education more accessible and engaging.
In the workplace, VR is emerging as a powerful tool for remote collaboration and training. With more companies adopting hybrid or fully remote models, VR meetings create a sense of presence that video calls often lack. Colleagues can interact in 3D virtual environments, brainstorming ideas on virtual whiteboards or walking through digital prototypes. Beyond meetings, VR training programs are revolutionizing skill development across industries. For example, construction workers can learn to operate heavy machinery safely, while customer service teams can simulate real-world interactions to refine their communication skills. The ability to practice complex tasks in a risk-free virtual environment enhances productivity and reduces costly errors.
Healthcare is another sector that stands to benefit immensely from VR. Beyond surgical training, VR is being used in therapy and rehabilitation. Patients recovering from strokes or injuries can engage in physical therapy exercises through VR programs that provide real-time feedback and motivation. Mental health treatments are also seeing innovations through VR, where patients with anxiety disorders or phobias confront their triggers in controlled, virtual environments. Such applications not only improve outcomes but also make treatments more accessible, as patients can participate from home under professional supervision.
VR is also reshaping entertainment and social interactions. The gaming industry, while the initial driving force behind VR adoption, is now just one piece of the puzzle. Virtual concerts, art exhibitions, and social meetups are becoming increasingly popular, allowing people to experience events without physical constraints. Social VR platforms enable users to meet friends, attend virtual parties, or even collaborate on creative projects in shared virtual spaces. These immersive experiences foster new forms of human connection, especially in times when physical gatherings may be limited.
Retail and commerce are seeing significant VR transformations as well. Virtual stores allow consumers to explore products in 3D before making a purchase, enhancing the online shopping experience. Shoppers can try on clothing virtually, view furniture in their homes, or test out gadgets, reducing uncertainty and improving customer satisfaction. This level of interactivity bridges the gap between physical and digital shopping, potentially transforming how people engage with brands and products.
Despite its promise, the widespread adoption of VR in everyday life faces challenges. Hardware costs, software development, and user comfort remain barriers for many consumers. Additionally, ethical concerns around privacy, data security, and the psychological effects of prolonged VR usage must be addressed as the technology becomes more prevalent. Companies and developers must prioritize accessibility, safety, and inclusivity to ensure that VR benefits society as a whole.
Looking forward, VR is likely to converge with other emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), creating even more integrated and intelligent experiences. Smart homes could leverage VR for immersive control of devices, while AI-driven virtual assistants might guide users through virtual environments tailored to their personal needs. This convergence promises a future where digital and physical realities blend seamlessly, enhancing productivity, entertainment, and social interactions in everyday life.
In conclusion, Virtual Reality is no longer confined to niche gaming applications—it is steadily becoming a transformative force in education, work, healthcare, retail, and social life. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, VR is poised to enrich our daily experiences, offering immersive, interactive, and meaningful engagements with the world around us. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are profound. The future of VR in everyday life is not just a possibility; it is an unfolding reality that promises to change the way we learn, work, play, and connect in the years to come. As we stand at the threshold of this digital frontier, one thing is clear: Virtual Reality will redefine the boundaries of everyday human experience, making the ordinary extraordinary.